题目
Find the kth largest element in an unsorted array. Note that it is the kth largest element in the sorted order, not the kth distinct element.
For example, Given [3,2,1,5,6,4] and k = 2, return 5.
Note: You may assume k is always valid, 1 ≤ k ≤ array’s length.
朴素暴力法
最简单直接的方法:排序,然后找出第k个元素。
public class Solution {
public int findKthLargest(int[] nums, int k) {
Arrays.sort(nums);
return nums[nums.length-k];
}
}
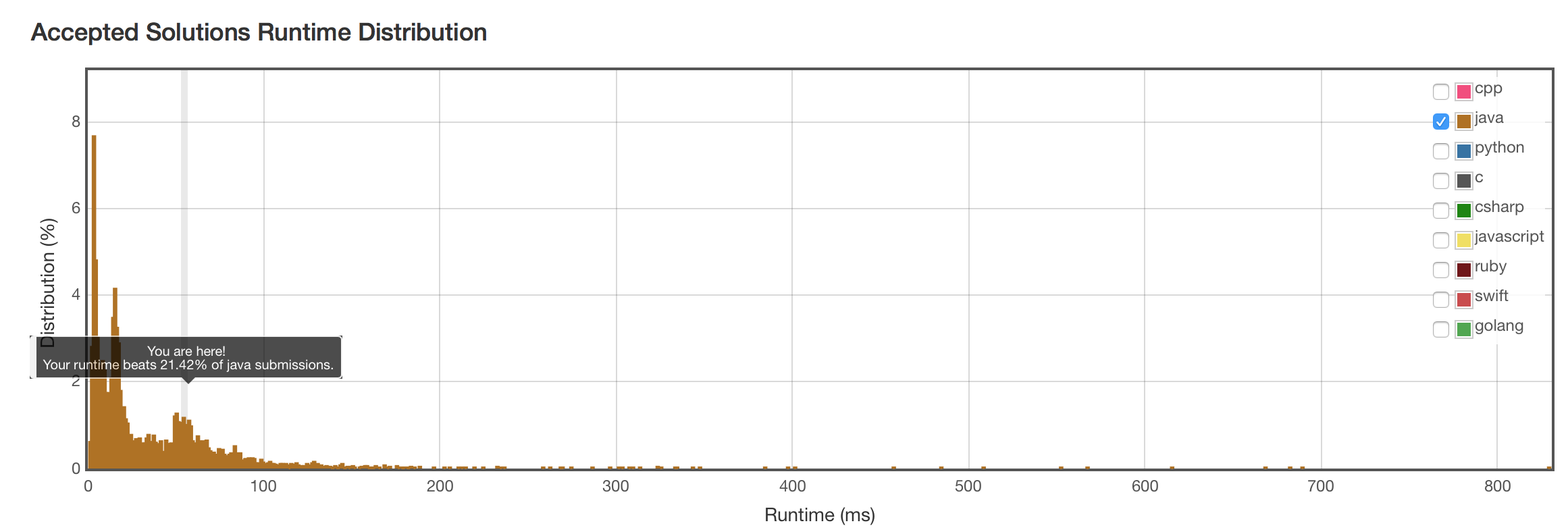
朴素法结果
暴力法结果非常好。就算算上C和C++,Java的Arrays.sort()函数的效率还是领先的。优化做的不错。
二分法
利用快排中分区(3-way-partition) 的思想,把一个数组划分成3部分:< pivot, pivot, > pivot的元素。
思路是:每做一次分区,就比较一下pivot和k的大小,然后舍弃pivot两边的其中一半。
注意! 前提是数组中没有重复的数字。如果数字可以重复,则方法无效。
二分法代码
还是使用了递归。
public class Solution {
public int findKthLargest(int[] nums, int k) {
return findKthSmallest(nums,0,nums.length-1,nums.length-k);
}
public int findKthSmallest(int[] nums, int low, int high, int k) {
int pivot = partition(nums,low,high);
if (pivot == k) {
return nums[pivot];
} else if (pivot < k) {
return findKthSmallest(nums,pivot+1,high,k);
} else {
return findKthSmallest(nums,low,pivot-1,k);
}
}
public int partition(int[] nums, int low, int high) {
if (low == high) { return low; }
int bound = low - 1;
int pivot = nums[high];
for (int i = low; i < high; i++) {
if (nums[i] <= pivot) {
bound++;
exchange(nums,bound,i);
}
}
bound++;
exchange(nums,bound,high);
return bound;
}
public void exchange(int[] nums, int i, int j) {
int temp = nums[i];
nums[i] = nums[j];
nums[j] = temp;
}
}
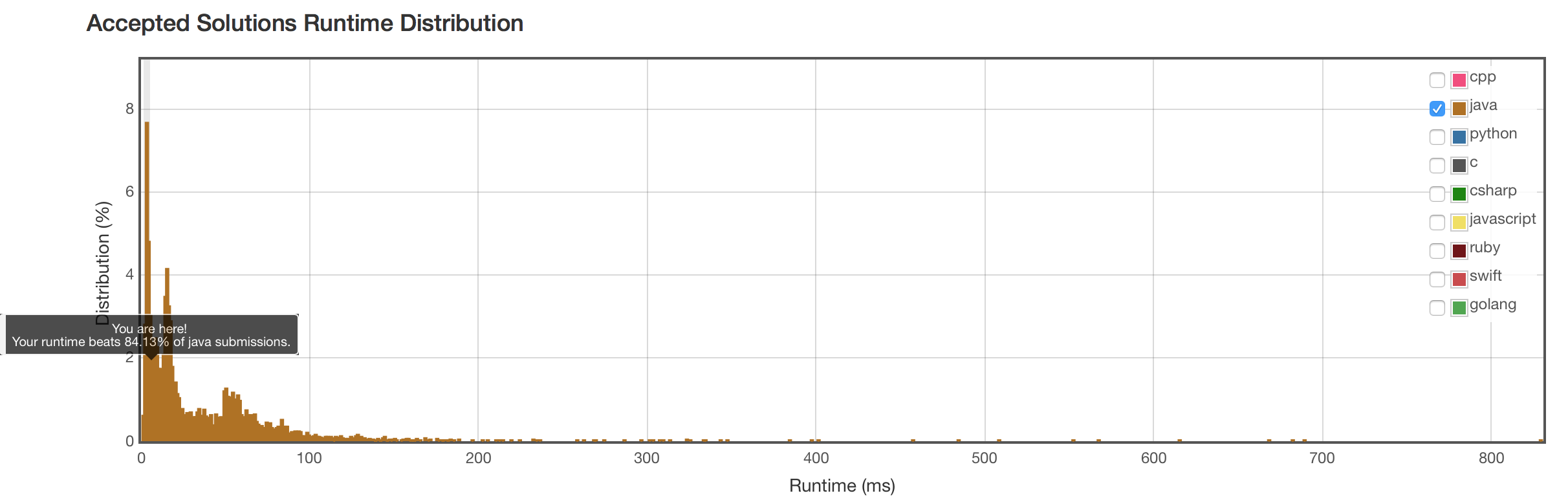
二分法结果
复杂度也是O(nlog(n)),但结果没有暴力排序法好。主要因为函数调用的开销,以及javasort()函数自身优化的优势。